Let’s be real for a second. You’ve probably tried the “eat less, move more” mantra. You’ve swapped your evening chai for green tea, maybe even tried skipping dinner. Yet, the scale refuses to budge. Or worse, it drops for a week and then bounces back with a vengeance.
Here’s the thing: In the high-stress, carb-heavy landscape of modern India, generic weight loss advice often fails. Why? Because it ignores the biological math unique to your body.
If you don’t know your numbers, you’re flying blind. The secret isn’t just “dieting”—it’s understanding your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR). This isn’t just another fitness buzzword; it is the financial budget for your body’s energy. If you are serious about transforming your health in 2026, mastering the bmr calculator weight loss india fitness framework is the single most effective step you can take today.
In this guide, we aren’t just giving you a formula. We’re going to show you how to apply it to a real Indian lifestyle—navigating weddings, office parties, and home-cooked meals—to get results that actually stick.
📑 What You’ll Learn
The Science: BMR vs. TDEE Explained
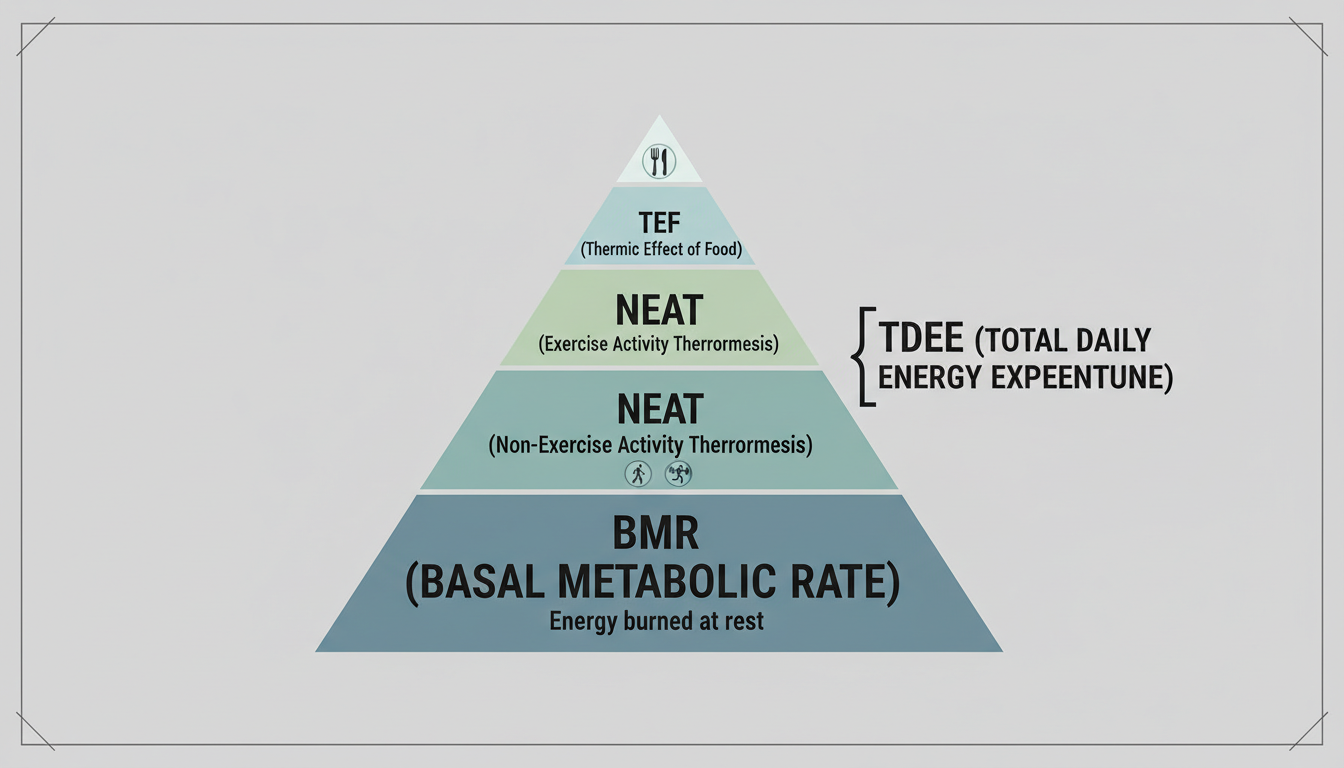
Think of your body like a car. Even when it’s parked in the garage with the engine idling, it’s burning fuel. That’s your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR).
Your BMR represents the number of calories your body burns just to stay alive—keeping your heart beating, lungs breathing, and brain firing. Surprisingly, this accounts for about 60% to 75% of your total daily energy burn. If you were to lay in bed all day watching Netflix without moving a muscle, you’d still burn your BMR.
However, you don’t just lay in bed. You walk to the train station, you type emails, you digest food, and maybe you hit the gym. When you add all that movement to your BMR, you get your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE).
🎯 Key Takeaway
Your BMR is your coma calories—what you burn at complete rest. Your TDEE is your maintenance calories—what you burn living your life. To lose weight, you must eat below your TDEE but ideally above your BMR.
The Indian Paradox: Why We Struggle with BMR
In our experience working with clients across India, we see a recurring pattern. The standard bmr calculator weight loss india fitness approach often clashes with cultural dietary habits.
Traditional Indian diets are incredibly nutrient-dense but can be calorically deceptive. A “healthy” home-cooked meal of rice, dal, and sabzi is often 70% carbohydrates. While delicious, this can spike insulin and make staying within a calorie deficit difficult without feeling hungry.
Furthermore, we have a “protein gap.” Most vegetarians in India believe dal is a high-protein source. In reality, dal is primarily a carbohydrate with some protein. To get 25g of protein from dal, you’d have to eat a quantity that comes with a massive calorie tag.
| Food Item (Standard Serving) | Primary Macro | Caloric Density | Metabolic Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| White Rice (1 bowl) | Carbohydrate | High | Low satiety, quick energy spike |
| Dal / Lentils (1 bowl) | Carb + Protein | Medium | Moderate satiety, often cooked with oil/ghee |
| Paneer (100g) | Fat + Protein | High | High satiety, but calorie-dense due to fat |
| Chicken Breast (100g) | Protein | Low | High thermic effect (burns more calories to digest) |
Step-by-Step: How to Use the BMR Calculator Weight Loss India Fitness Framework
Ready to crunch the numbers? You don’t need a PhD in math. You just need to follow this workflow. We recommend using the Mifflin-St Jeor equation, which studies have shown to be the most accurate for modern populations.
Step 1: Find Your Baseline
Use a reliable tool like the BMR Calculator. You will need your:
- Current Weight (be honest!)
- Height (in cm)
- Age
- Gender
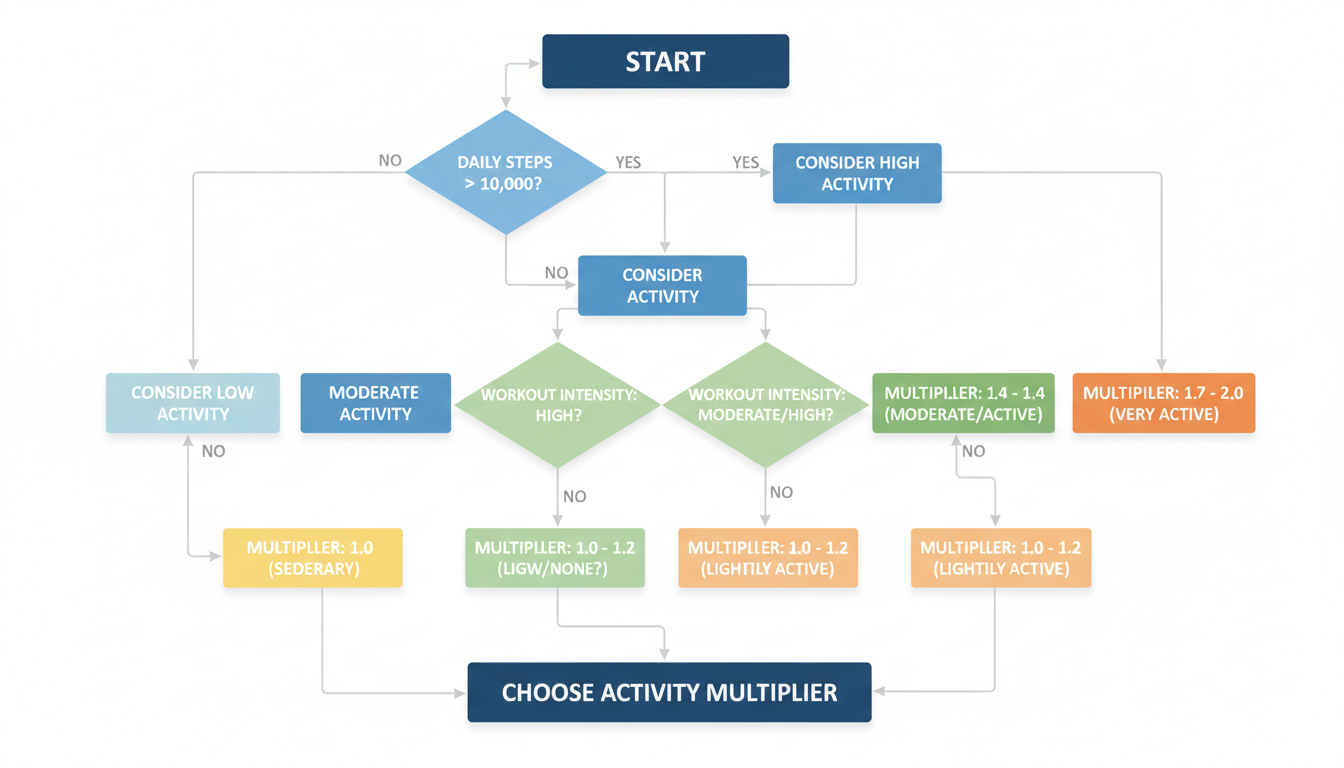
Step 2: Apply the Activity Multiplier
This is where 90% of people mess up. Be brutally honest here. Overestimating your activity is the fastest way to kill your weight loss progress.
⚠️ Watch Out
The “Office Worker” Trap: If you go to the gym for 45 minutes but sit at a desk for 9 hours, you are NOT “Moderately Active.” You are likely “Sedentary” or “Lightly Active.” That 45-minute workout burns fewer calories than you think.
Decoding Activity Levels for the Indian Lifestyle
To get the bmr calculator weight loss india fitness formula right, match your lifestyle to these descriptions:
| Activity Level | Multiplier | Typical Indian Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Sedentary | 1.2 | Desk job (IT/Corporate), commute by car/bike, no intentional exercise. |
| Lightly Active | 1.375 | Desk job, but you take public transport (walking to station) or do yoga/light walking 2-3x a week. |
| Moderately Active | 1.55 | Active job (sales/fieldwork) OR desk job + intense gym/sports 3-5 days a week. |
| Very Active | 1.725 | Construction/Manual labor OR intense training 6-7 days a week (athlete level). |
Structuring Your Deficit: The Safe Way
Once you have your TDEE, the math is simple but strict. To lose fat, you need a deficit. To gain muscle, you need a surplus.
The Golden Rule: Aim for a deficit of 300–500 calories below your TDEE.
For example, if your TDEE is 2,200 calories:
- Target Intake: 1,700 – 1,900 calories.
- Result: Sustainable loss of 0.3kg to 0.5kg per week.
Do not drop your calories to 1,200 just because you read it in a magazine. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, drastic caloric restriction can slow your metabolism, making it harder to keep weight off long-term.
💡 Pro Tip
Focus on NEAT (Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis): Instead of adding more gym time, increase your daily movement. Stand while taking calls, take the stairs instead of the elevator, or park your car further away. These “micro-movements” can burn an extra 200-300 calories a day without fatigue.
The Role of Protein and TEF
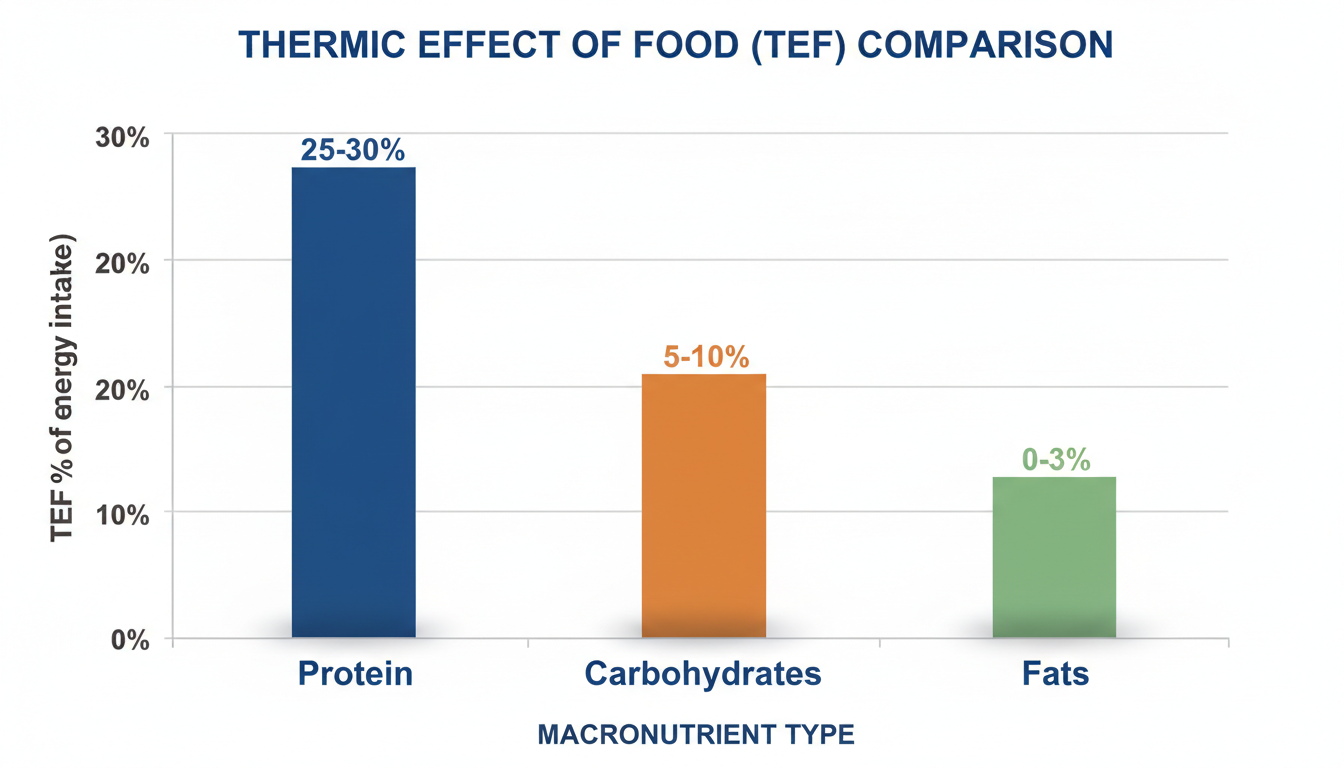
Here is a secret weapon for your bmr calculator weight loss india fitness plan: The Thermic Effect of Food (TEF). Your body burns energy just to digest food.
- Fats: 0-3% of calories burned in digestion.
- Carbs: 5-10% of calories burned in digestion.
- Protein: 20-30% of calories burned in digestion.
By increasing your protein intake (paneer, soya, chicken, fish, whey), you literally boost your metabolism. It’s like getting a discount on the calories you eat.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
Does eating late at night affect my BMR?
Technically, your BMR stays relatively constant. However, eating heavy meals late at night can disrupt sleep quality. Poor sleep increases cortisol and hunger hormones the next day, which can indirectly ruin your calorie deficit. It’s not the time you eat, but the total quantity that matters most.
I calculated my BMR, but I’m not losing weight. Why?
This is usually due to one of two things: either you are underestimating how much you eat (hidden calories in oil, sugar in tea, “healthy” snacks), or you have overestimated your activity level. Try tracking your food intake meticulously for one week using a kitchen scale to find the discrepancy.
Should I eat back the calories I burn at the gym?
Generally, no. Fitness trackers often overestimate calories burned by up to 30%. If your tracker says you burned 500 calories, it’s safer to assume you burned 300. If you eat back all 500, you might erase your deficit entirely. Treat exercise calories as a “bonus” for faster weight loss, not a license to eat more.
How often should I recalculate my BMR?
As you lose weight, your body requires less energy to function. We recommend recalculating your BMR and TDEE after every 5kg of weight loss. This prevents the dreaded “plateau” where your weight loss stalls because your intake now matches your new, lower maintenance needs.
Conclusion: Your Roadmap to a Fitter 2026
Mastering your weight isn’t about starving yourself or spending three hours a day in the gym. It’s about data. It’s about understanding the inputs and outputs of your own body.
The bmr calculator weight loss india fitness strategy gives you control. It moves you away from emotional eating and towards logical nutrition. Remember, the best diet is the one you can stick to for the long haul. Start by calculating your numbers today, be honest about your activity, and prioritize protein in your meals.
Don’t let another year slip by guessing. Use the tools available, trust the science, and watch your body transform.
Ready to optimize other areas of your life? Check out our EMI Calculator for financial health or explore our guide to AI tools to boost your productivity.



